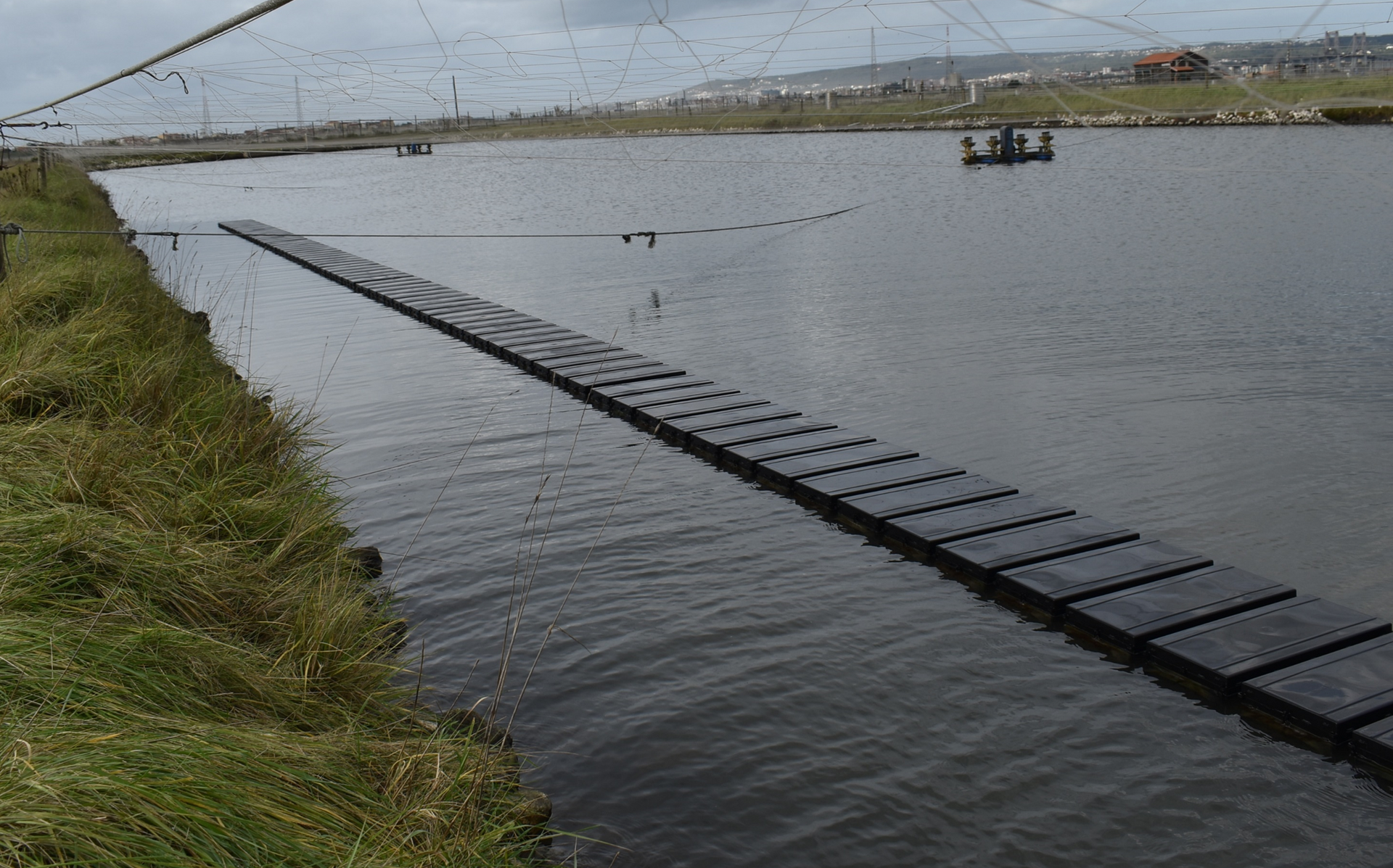
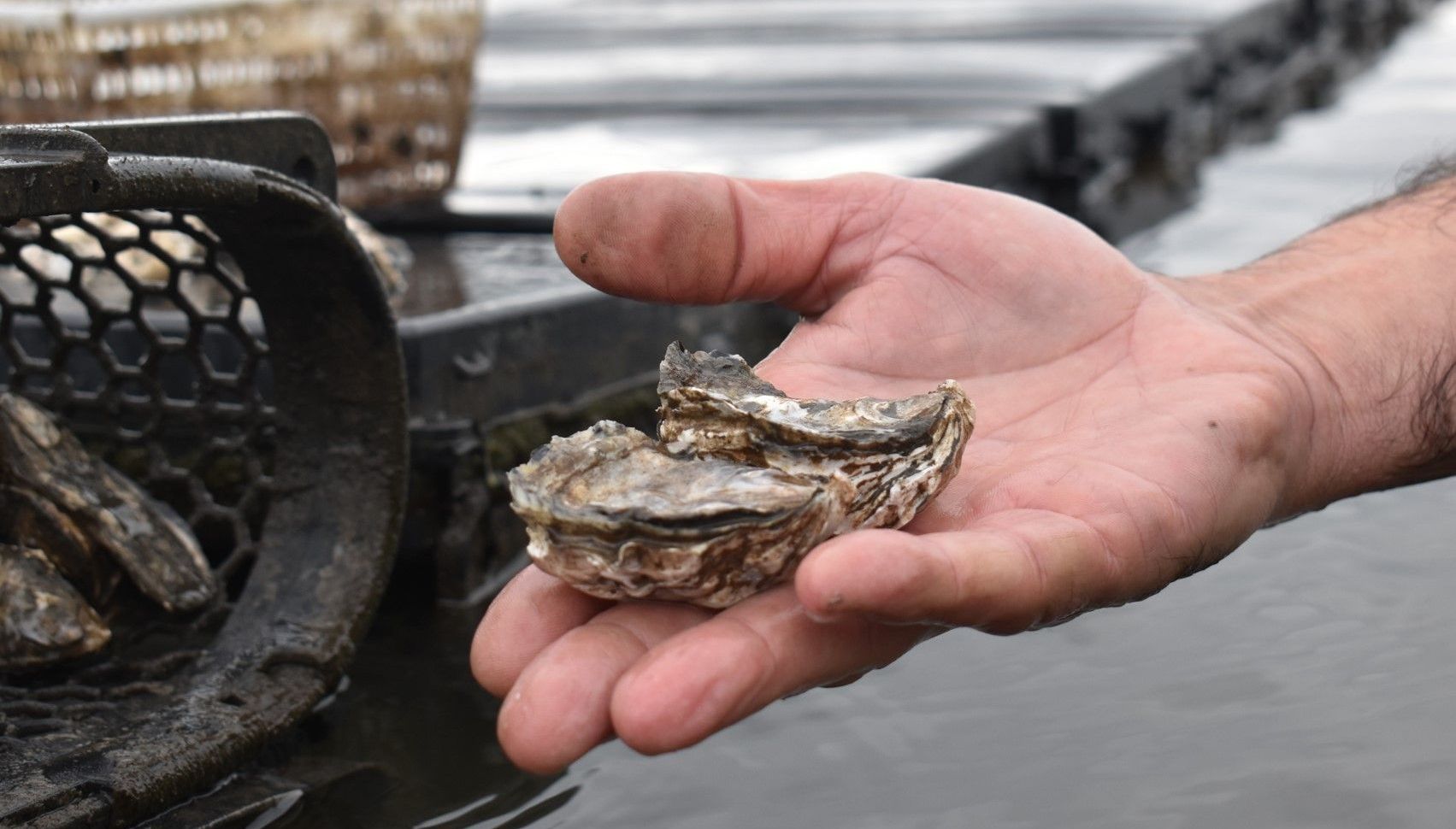
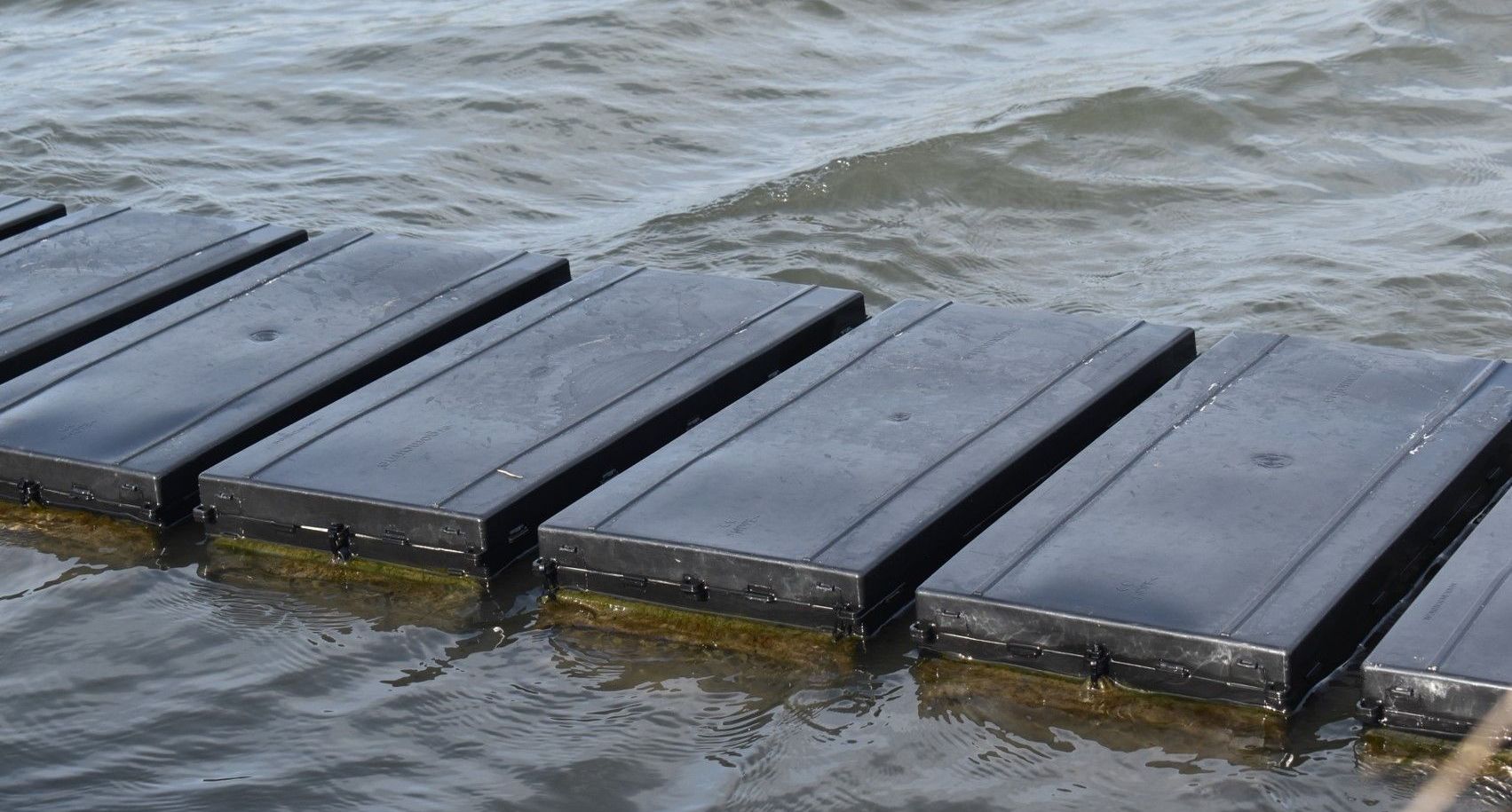
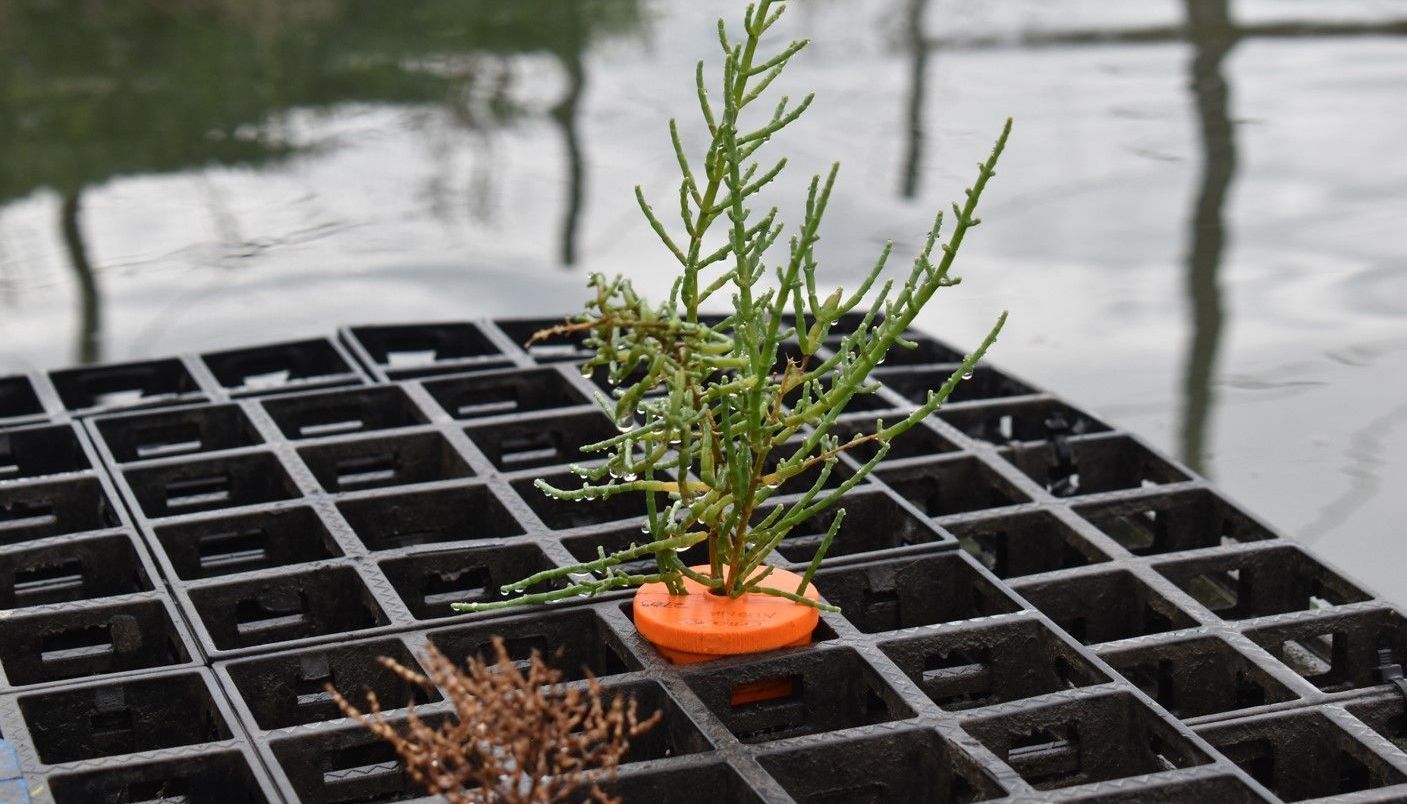
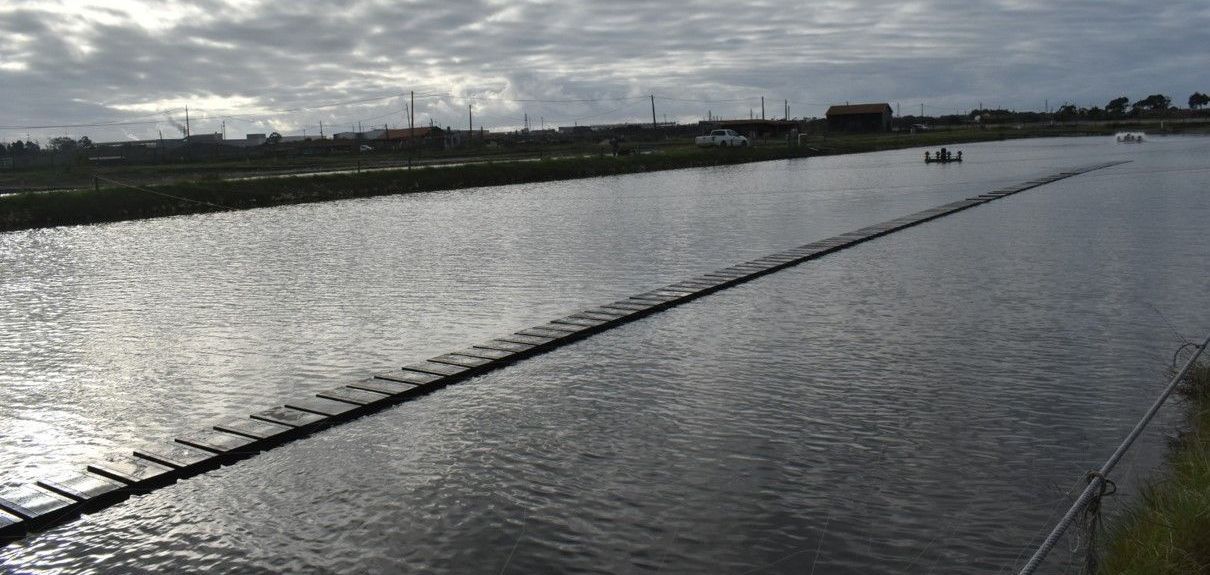
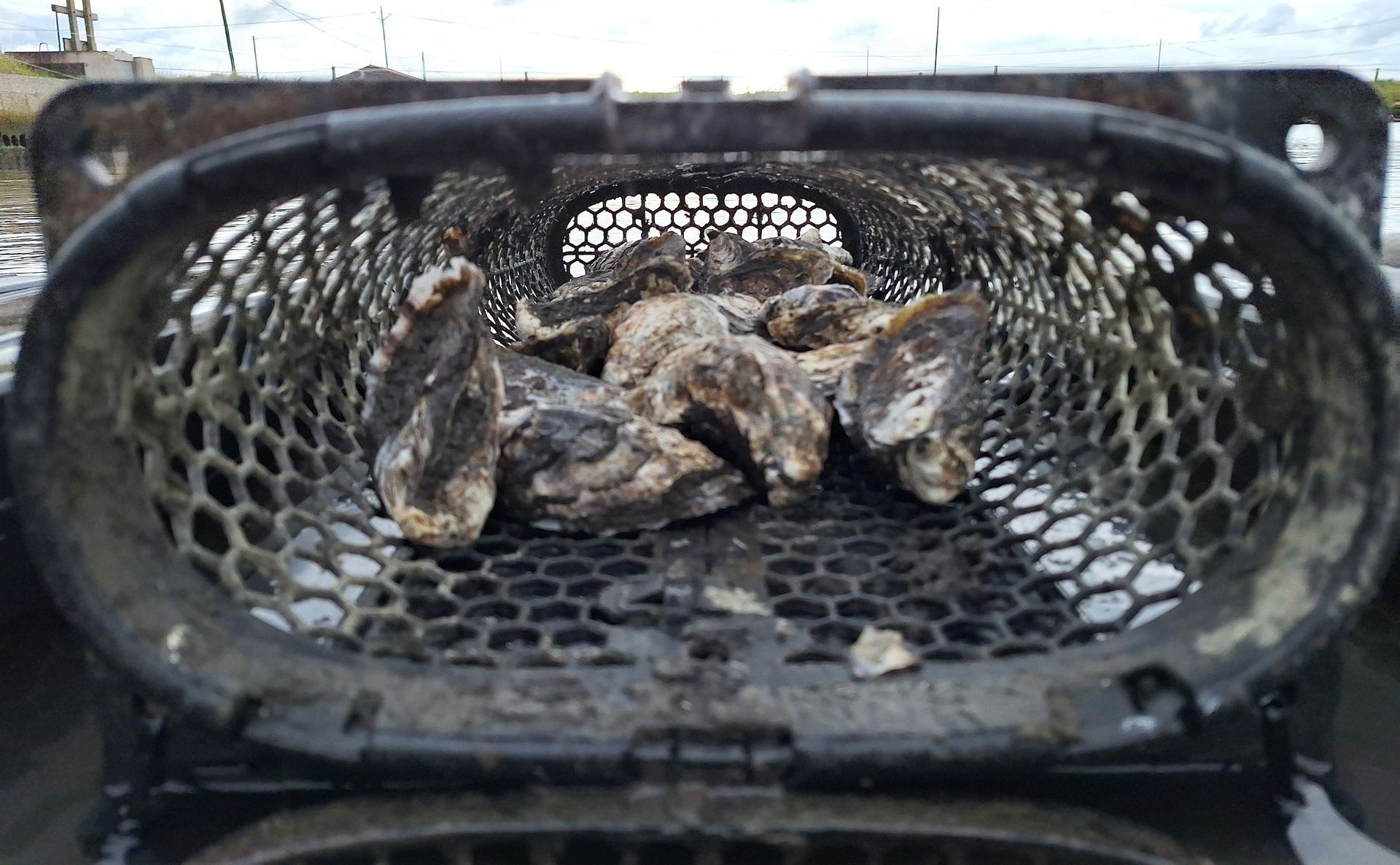
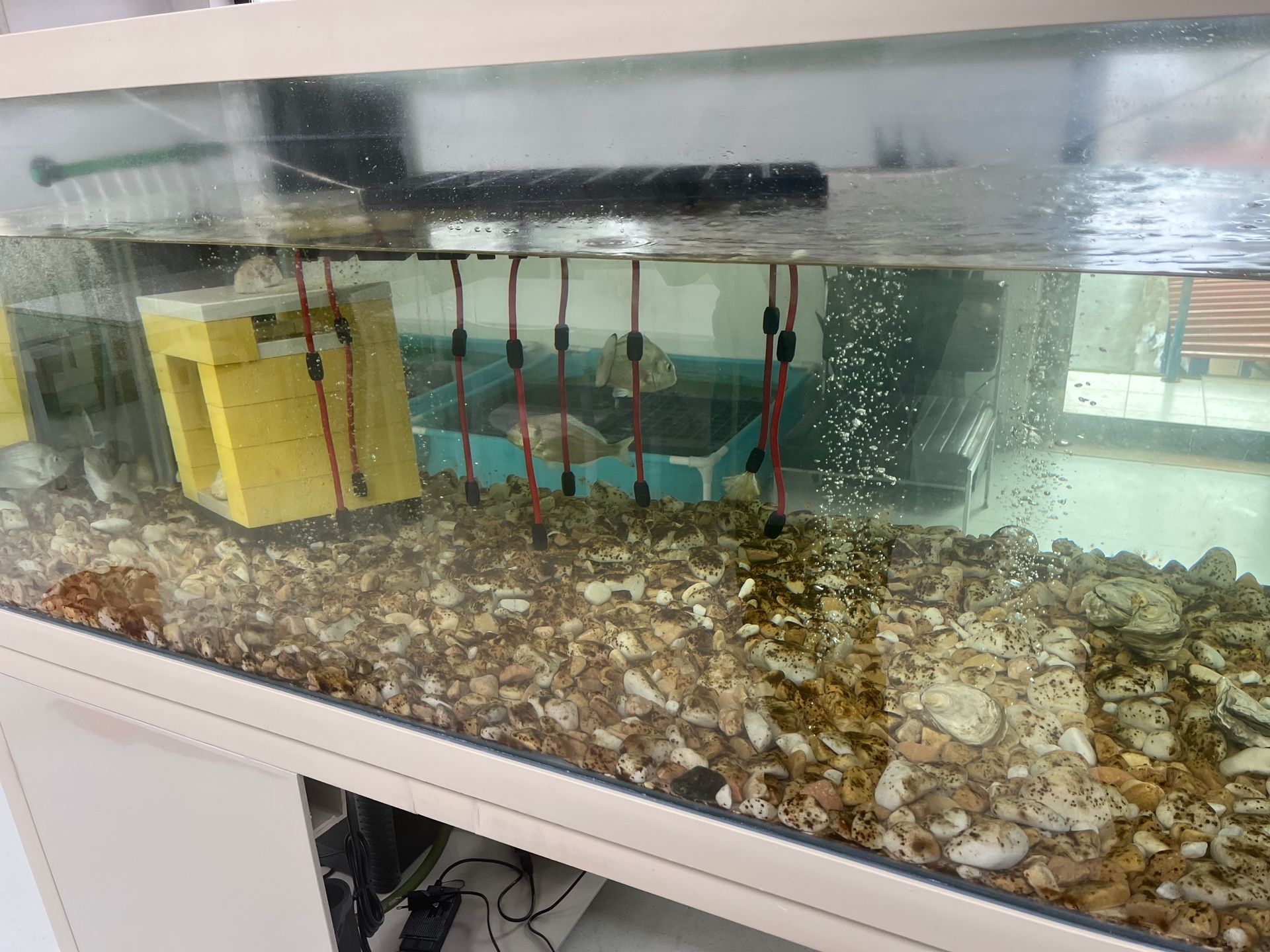
Our Aquarium
Since installing our aquarium, we have been conducting indoor tests simulating a natural multitrophic environment, while observing the well-being of the resident animals (Sparus aurata and Craossotea magallana) and the balance of this micro-ecosystem. We are partners with the Fish Etho Group in the AquaReach project, studying animal well being. One theme that this observation raised for us was the concept of Ethology, which we intend to explore further. We imagine the aquarium as an amusement park for the fish residing there, which have effectively gone from an initial state of apparent "stress" and depression to a quite active state of exploring the props we have placed there, with the help of, among other things, 3D printing and Oikum structures.